Consensus is one of the key issues in blockchain technology which must be resolved since it is a security measure and a guarantee of the system integrity. On the other hand, Fantom, which is one of the highly recognized names in the blockchain sphere, utilizes Lachesis, a novel consensus mechanism that speeds up transactions and results in a more dependable network.
Fantom and the Decentralized Consensus
The essence of consensus in decentralized systems implies the participants of a blockchain agreeing on a single chain that records all transactions correctly. Moreover, this agreement is the key component for the abatement of harmful activities and building trust in the network. Fantom’s Lachesis consensus mechanism stands apart for its efficiency and resilience by incorporating elements like Asynchronous Byzantine Fault Tolerance (aBFT) and directed acyclic graphs (DAGs).
8/ For a deeper exploration of the topics discussed above, see below.
💻 Sonic technology:https://t.co/4WKswzGAzf
✅ Opera consensus:https://t.co/oEkDQzZ9am
— Fantom Foundation (@FantomFDN) April 25, 2024
One of the foundational pillars of Fantom’s consensus model is Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (pBFT). This mechanism empowers decentralized systems to function seamlessly even in the presence of malicious or faulty nodes. In a pBFT system, nodes communicate extensively to establish consensus on the network’s state and transactions. In addition, this robust communication protocol ensures that bad actors cannot manipulate the system’s integrity.
Asynchronous Byzantine Fault Tolerance (aBFT)
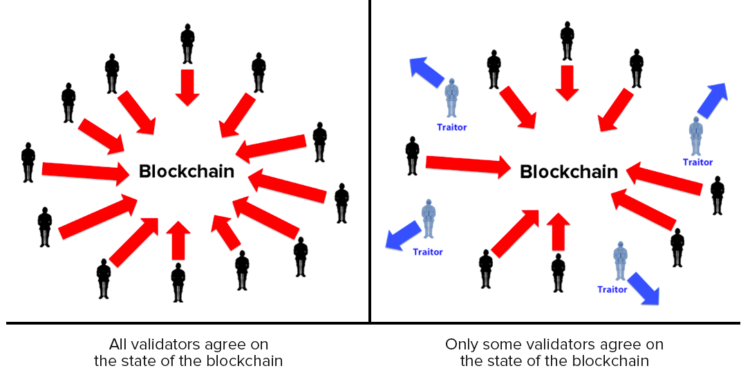
The innovation of Fantom extends to Asynchronous Byzantine Fault Tolerance (aBFT), a cutting-edge approach to achieving consensus. Unlike traditional BFT systems, aBFT allows nodes to reach consensus independently without strict sequential order requirements. However, this asynchronous nature enhances transaction speed and overall network efficiency, making Fantom a frontrunner in scalable blockchain solutions.
Directed Acyclic Graphs (DAGs)
Another key component in Fantom’s consensus mechanism is the utilization of directed acyclic graphs (DAGs). DAGs provide a flexible and non-linear structure for organizing transactions, allowing for concurrent block creation and faster validation. Moreover, this architecture significantly improves throughput and reduces latency compared to traditional blockchain structures.

To complement its consensus mechanism, Fantom adopts a proof-of-stake (PoS) approach. PoS requires validators to stake tokens as collateral, incentivizing them to act honestly and validate transactions accurately. This economic model, coupled with Fantom’s robust consensus algorithm, creates a secure and efficient environment for decentralized applications (dApps) and token transfers.
How Fantom Transaction Process Achieve Speed and Security?
The full understanding of Fantom’s consensus algorithm cannot be completed if you do not know the details of its transaction process. Users’ transactions on Fantom undergo a fast travel, from submission to confirmation and then addition to the main chain.
 The smooth combination of DAG-based consensus and PoS leads to swift transaction finality and network scalability. Moreover, Fantom’s Lachesis is a consensus protocol that is different from the rest of blockchain protocols in their way of operation. Fantom employs cutting-edge technologies including aBFT, DAGs, and PoS. This ensures that the platform is robust, secure and scalable in nature. Since the blockchain space is not stagnant, Fantom is still at the forefront of the technological world and the digital era, and is the creator of a consensus mechanism that is suitable to the digital world.
The smooth combination of DAG-based consensus and PoS leads to swift transaction finality and network scalability. Moreover, Fantom’s Lachesis is a consensus protocol that is different from the rest of blockchain protocols in their way of operation. Fantom employs cutting-edge technologies including aBFT, DAGs, and PoS. This ensures that the platform is robust, secure and scalable in nature. Since the blockchain space is not stagnant, Fantom is still at the forefront of the technological world and the digital era, and is the creator of a consensus mechanism that is suitable to the digital world.